Diesel forklifts Assembly lines
Diesel forklifts are industrial material handling vehicles powered by diesel engines and are widely used in logistics and warehousing industries. Here is an introduction to the types, structure, detailed assembly production process, and production line equipment of diesel forklifts:
Types of Diesel Forklifts:
- Counterbalanced Diesel Forklifts: The most common type, with counterweights at the rear to maintain stability, suitable for various working environments and load requirements.
- Container Forklifts: Designed specifically for moving containers, with a high lifting height and strong load capacity, used in ports, docks, and other places requiring large-scale container handling.
- Side Loaders: Used for lifting and moving containers, capable of lifting directly from the side or front of the container without turning it over, greatly improving work efficiency.
- Rough Terrain Forklifts: Designed for complex terrain and harsh environments, with strong off-road capabilities and high reliability, used in construction sites, mines, and other places requiring work in complex terrains.
Structural Components:
- Engine: The power source of the diesel forklift, converting thermal energy into mechanical energy.
- Chassis: Includes the walking mechanism, serving as the support and mobility base of the forklift.
- Cab: The operating platform, including the driver's cab and control parts.
- Lifting Mechanism: Includes forks and lifting cylinders, used for lifting and moving goods.
- Hydraulic System: Responsible for the forklift's lifting, tilting, and steering functions.
- Electrical Equipment: Includes batteries, motors, control systems, etc., especially in electric forklifts.
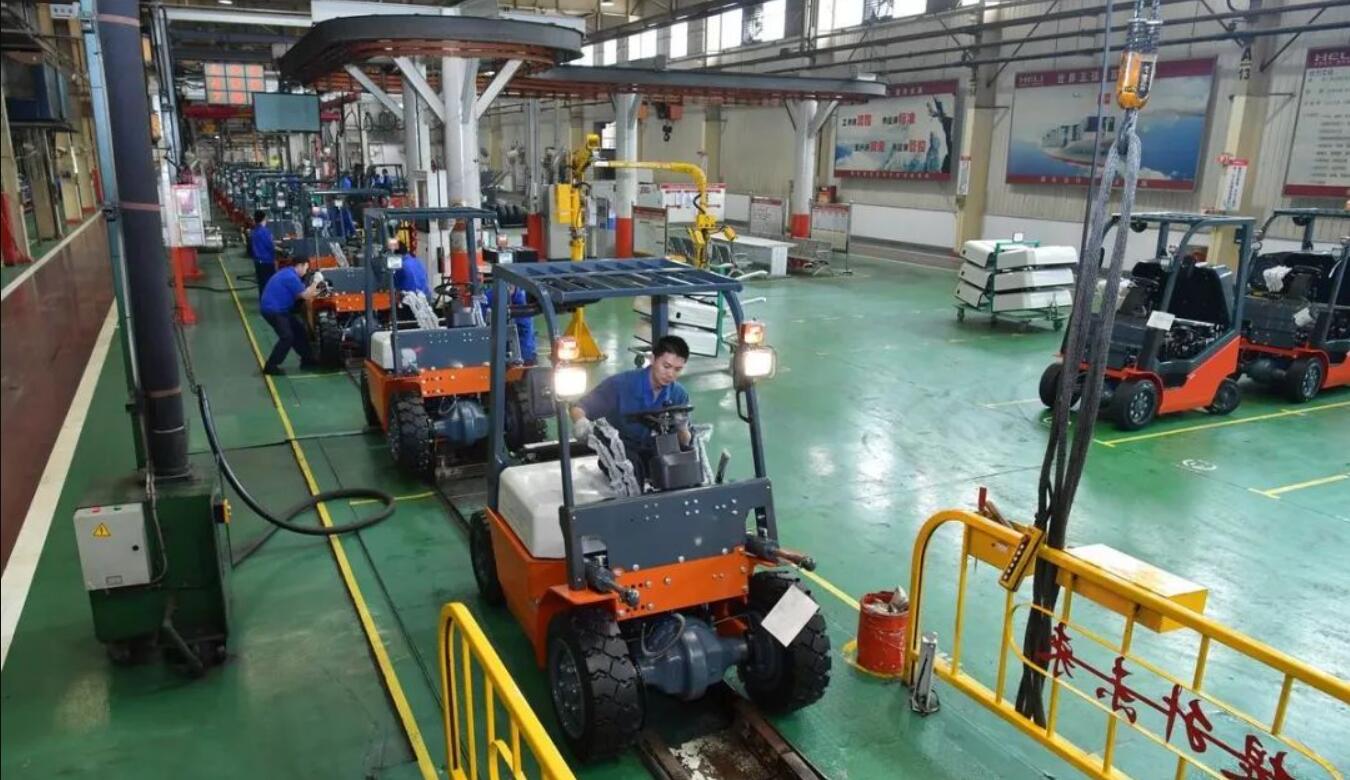

The assembly process of diesel forklifts is a complex industrial production process that involves multiple steps and precise craftsmanship.
-
Material Preparation: Before production begins, all necessary materials must be prepared, including steel, plastic, rubber, etc., typically purchased from suppliers.
-
Part Machining: Raw materials are processed into required parts, which may include casting, forging, and machining processes.
-
Component Pre-assembly: Key components such as gearboxes and drive axles may be pre-assembled and tested before final assembly to ensure their performance and quality.
-
Frame Assembly: The frame is the foundational structure of the forklift and must be precisely assembled to ensure the vehicle's stability and durability.
-
Engine Installation: As the power source of the forklift, the engine must be accurately aligned and secured to the frame.
-
Hydraulic and Electrical System Installation: These systems are responsible for the forklift's lifting, tilting, and steering functions and must be installed and adjusted according to specific process requirements.
-
Cab and Control Installation: The installation of the cab must ensure the operator has a good view and comfortable operation.
-
Lifting Mechanism Assembly: This includes the installation of the fork and lifting cylinder, which is the key part for the forklift to handle the loading and unloading of goods.
-
Complete Machine Assembly: All parts and systems are assembled into a complete forklift, with strict quality control and inspection.
-
Testing and Adjustment: After production is completed, the forklift must undergo a series of functional tests, performance tests, and safety tests to ensure it meets work requirements.
-
Final Inspection and Delivery: Finally, the forklift will undergo a final inspection to confirm that all functions are normal and meet safety standards before being prepared for delivery to customers.