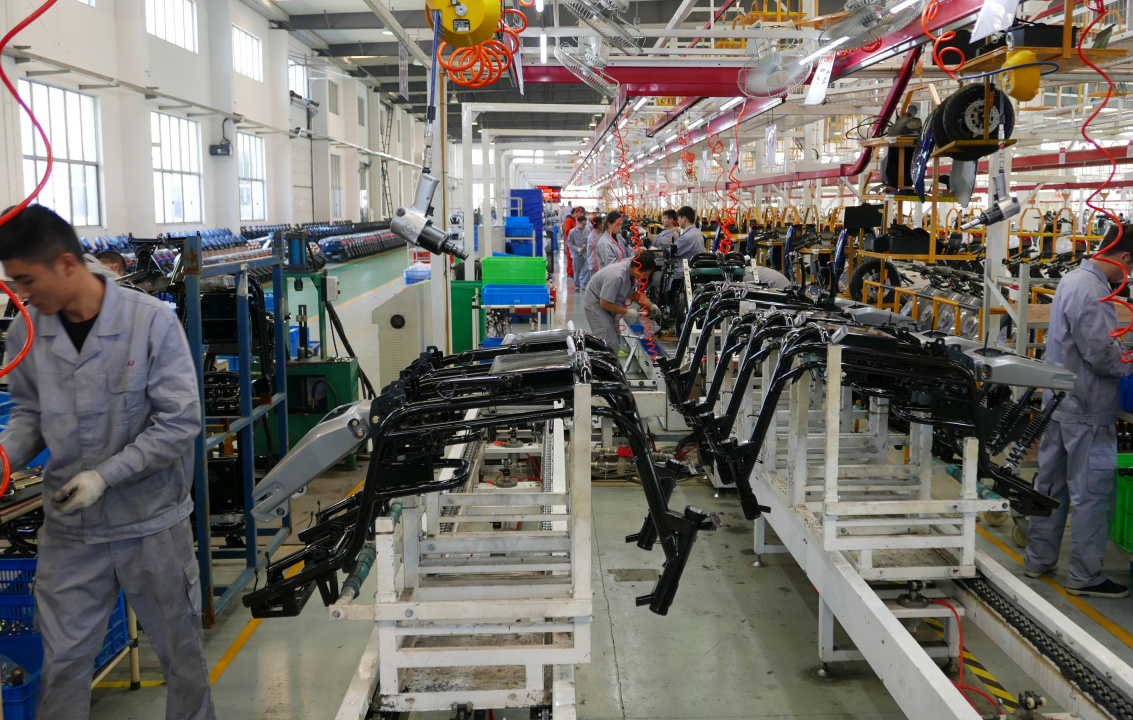
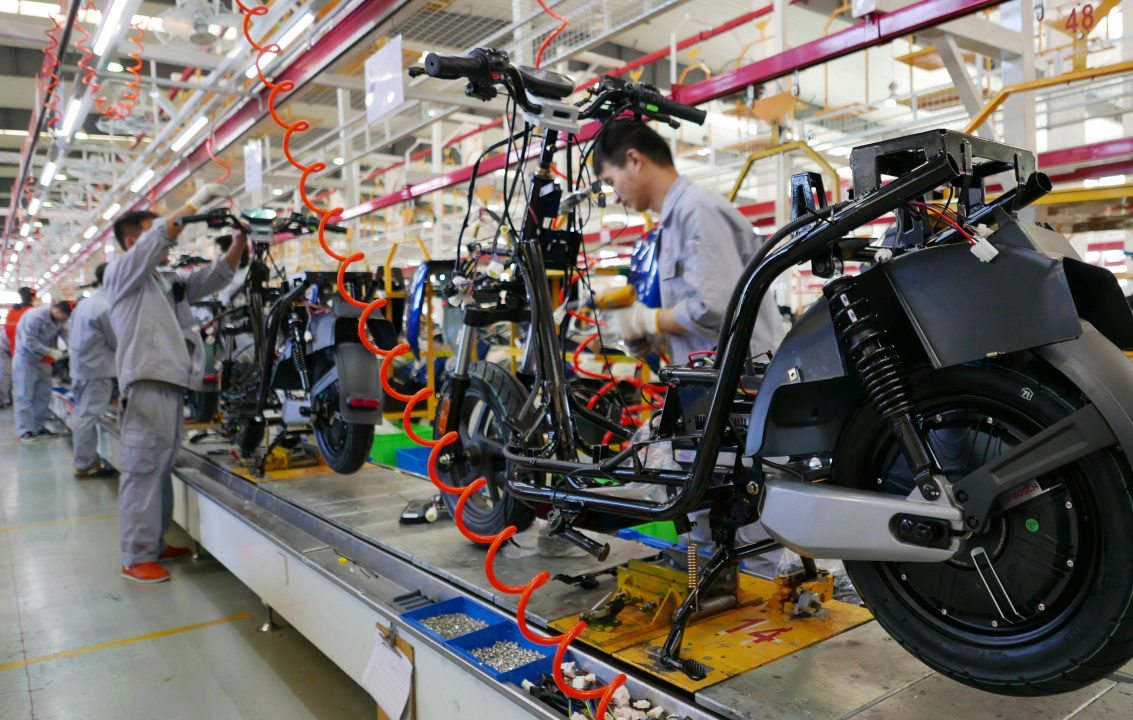
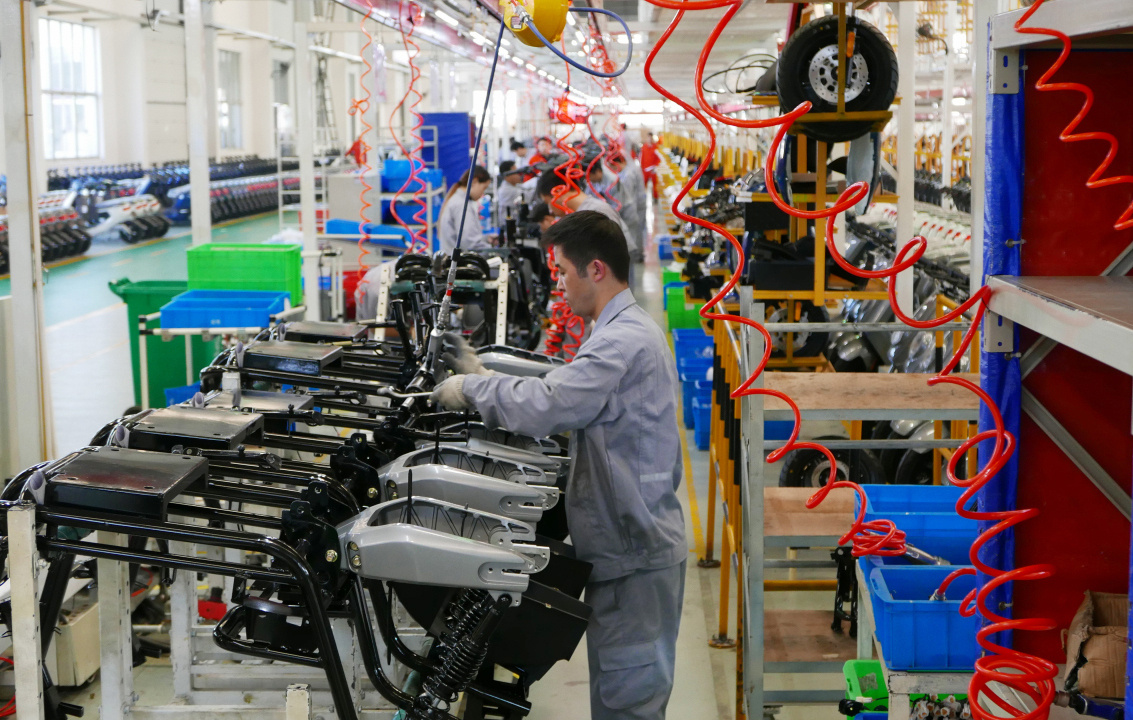
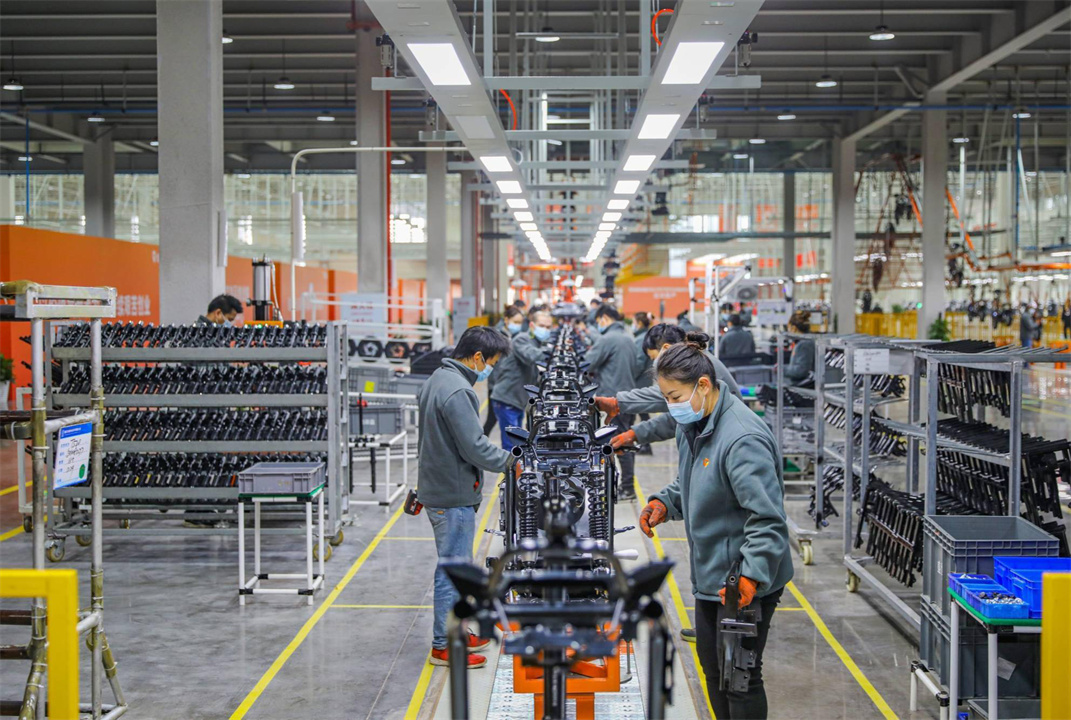
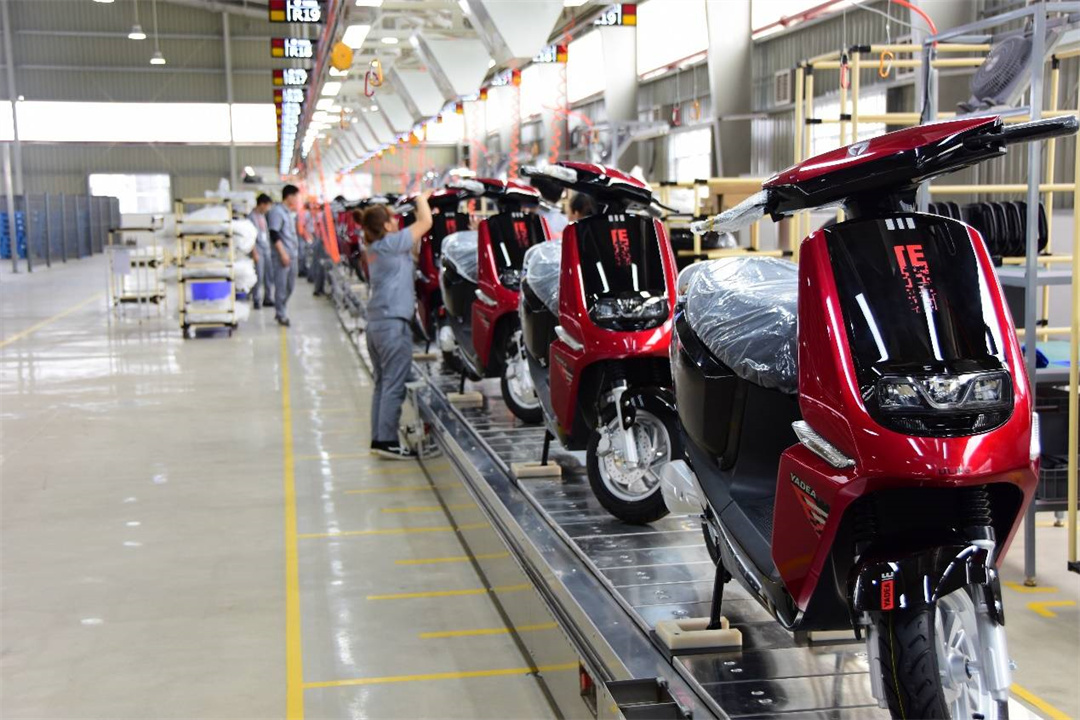
The structure, assembly process, and automated production line of a motorcycle are highly specialized manufacturing processes based on universal industrial standards and practices.
Motorcycle Structure
A motorcycle consists of the following main parts:
- Frame: Serves as the skeleton of the motorcycle, supporting all other components.
- Engine: Provides power, which can be an internal combustion engine or an electric motor.
- Transmission System: Includes gears, chains, belts, or shafts that transfer power to the wheels.
- Suspension System: Includes front forks and rear shock absorbers, providing a smooth ride.
- Braking System: Includes disc brakes or drum brakes, ensuring safe stopping.
- Electrical System: Includes battery, ignition system, lights, and signals.
- Fuel System: Includes fuel tank, fuel pump, and carburetor or fuel injection system.
- Wheels and Tires: Provide the point of contact for travel.
Assembly Process
The assembly process of a motorcycle typically includes the following steps:
- Engine Assembly: Assembling the crankcase, installing breather hoses, cleaning, and fitting the crankcase cover.
- Transmission System Assembly: Installing the gearbox, shifting mechanism, gear shafts, etc.
- Suspension and Braking System Assembly: Assembling front forks, rear shock absorbers, brakes, etc.
- Electrical System Assembly: Installing battery, motor, ignition system, lights, and signals.
- Fuel System Assembly: Installing fuel tank, fuel pump, carburetor, or fuel injection system.
- Wheel and Tire Installation: Installing front and rear wheels and their tires.
- Final Inspection and Adjustment: Ensuring all parts are correctly installed and necessary adjustments are made.
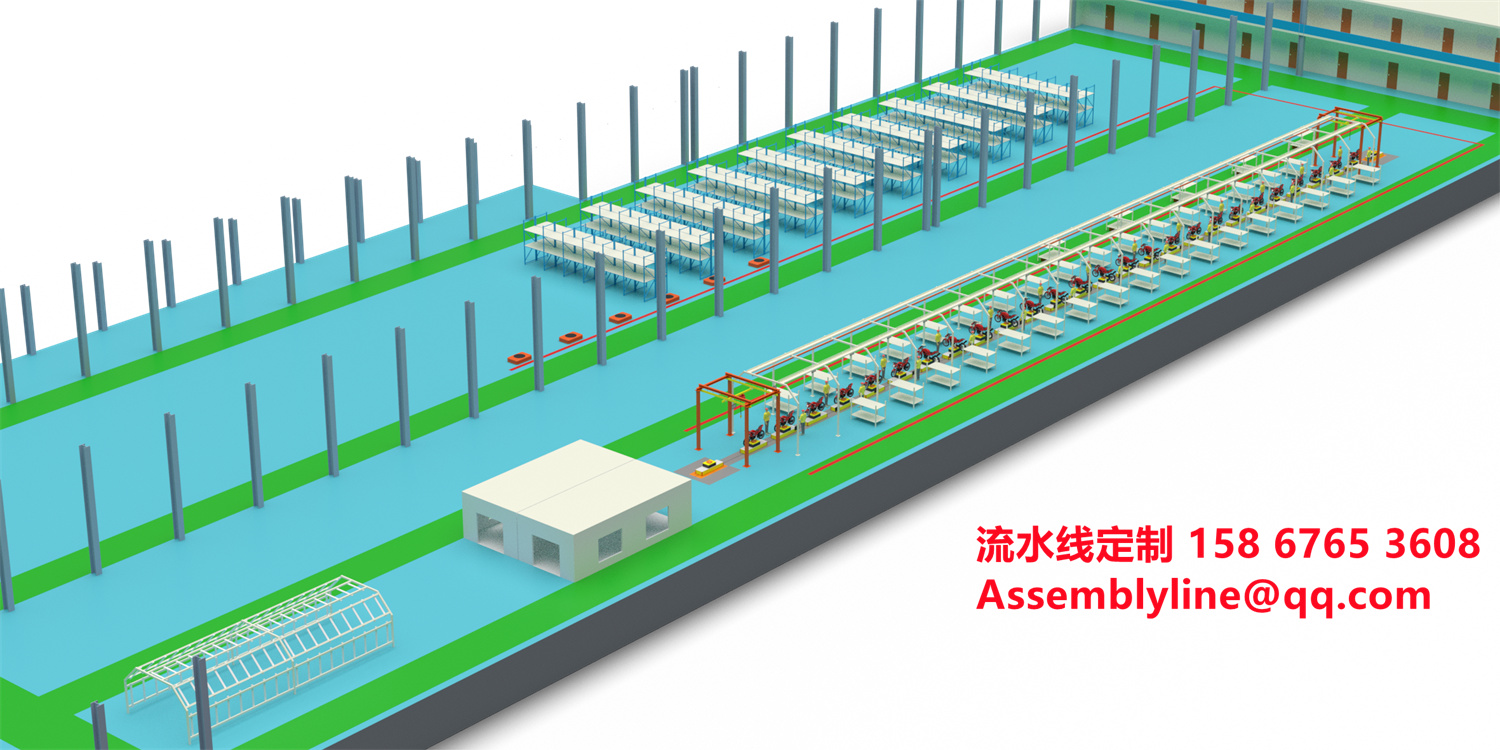
Automated Production Line
The design and implementation of an automated production line can improve production efficiency and product quality, typically including:
- Modular Workstations: Each workstation is responsible for specific assembly tasks.
- Conveyor Belt System: Moves the motorcycles between different workstations.
- Robotic Automation: Used for repetitive or precision assembly tasks.
- Quality Control System: Ensures each assembly stage meets quality standards.
- Customized Design: Customized production lines according to specific production needs and scale.
Automated production lines can increase production speed, reduce costs, and maintain consistent quality standards by reducing human intervention. Different manufacturers may adopt different automation solutions based on their specific production requirements and technical capabilities.
The motorcycle assembly line can be designed and planned in two key configurations: CKD (Completely Knocked Down) and SKD (Semi-Knocked Down). In CKD, motorcycles are fully disassembled into components and shipped to the assembly plant, where they are completely assembled from scratch. This approach is ideal for countries with a strong local manufacturing base and skilled labor force. On the other hand, SKD involves shipping partially assembled motorcycles, which are then completed at the destination. This method is cost-effective for countries with less developed manufacturing capabilities, as it requires less local assembly expertise. Both designs require careful planning to optimize assembly processes, minimize production time, and ensure quality standards are met.
Motorcycle Assembly line CKD SKD Design & Planning
Factory address: East Industrial Cluster, Wenling City, Zhejiang Province
Aircraft: Taizhou Luqiao Airport (1 hour) Wenzhou Airport (2 hours)
High speed rail: Wenling Station (40 minutes)
Expressway intersection: Wenling North (15 minutes) Wenling East (20 minutes)
Contact our engineering team and get company info
Email: Assemblyline@qq.com